TELANGANA / Pennsylvania, U.S.A:
‘In your final rest
on a rope-cot,
were you still dreaming
of a piece of bread?’

In your final rest on a rope-cot, were you still dreaming of a piece of bread? Beloved one, we the people of this country, of that country, can make anything but a piece of bread for you. --Evening with a Sufi: Selected Poems by Afsar Mohammad, translated from the Telugu by Afsar Mohammad & Shamala Gallagher, Red River Books, 2022.
These lines send shivers down the spine and recreate an empathetic longing for immigrant souls in search of succour. They also swiftly draw an image laced with poignancy — a loss, a regret, the economics that deny innovative young men their keep and force immigration in search of sustenance. Would the poet have been one of them?
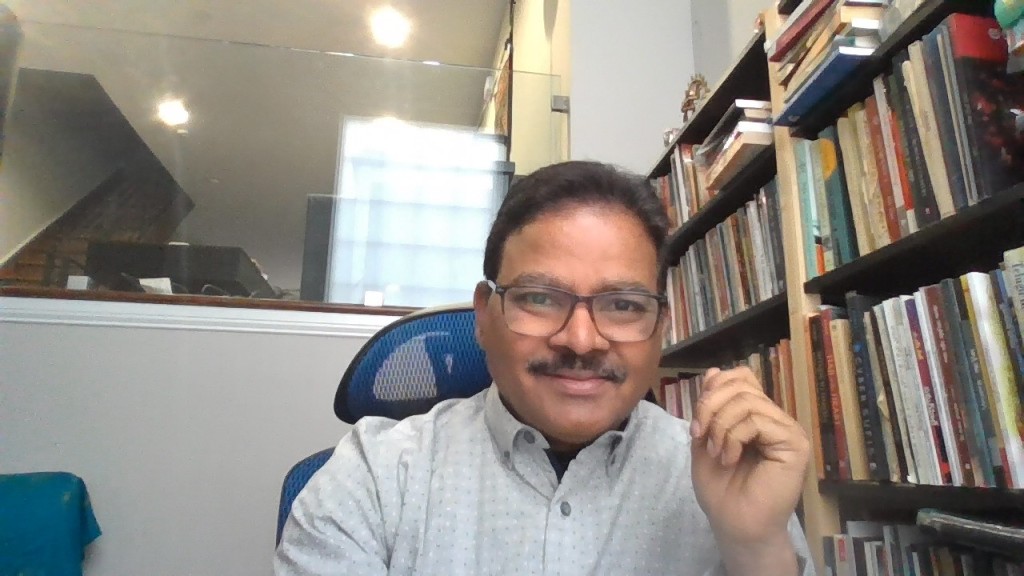
Travelling from a small village in the South Indian state of Telangana, Afsar Mohammad has journeyed across continents and now teaches South Asian Studies at the University of Pennsylvania. Known as a trendsetting poet and literary critic for post-1980s Telugu literature, Afsar has brought out five volumes of poetry, one collection of short stories and two volumes of literary theory essays. He is also a distinguished scholar of Indian studies and has published extensively with various international presses, including Oxford and Cambridge. He is currently working on a translation of Sufi poetry from Telugu to English. In this interview, we trace his growth as a writer and editor of the webzine, Saranga, which now seems to be transcending linguistic barriers to give voice to multiple cultures…
Tell us about your journey as a writer. When and how did it start?
It’s a long story, but to cut it short — the beginnings were somewhat puzzling… Inspired by Shakespearean sonnets, I first wrote some sonnets in English, and then switched to free verse. Since most of my friends in my high school started pushing me to write something in Telugu, I had to migrate to Telugu. Quite surprisingly, I was first published in English, and then it took me a while to get something published in Telugu. I had hard time getting published in Telugu due to its newness in expressions and most editors felt that there was nothing “Telugu” in that kind of writing. So, my early writings quite naturally found their home in some English journals!
Your poetry rings with the pain of distance, the pain and struggle from others’ suffering transcending your own self. What is the source of your inspiration — is it your past or your present?What affects you more — your being an immigrant or a Sufi?
We’re distanced by many things — not just physically! We live in many shattered and scattered worlds, and sometimes we fail to reflect on those worlds. I feel like I’m a constant immigrant — despite my formal citizenship and legal boundaries. Sufism is merely a segment of this expansive realm. Both past and present define our destiny, right?! Of course, I try to live in the present rather than in the past, but never deny the baggage of the past.
Why do you subscribe to the Sufi school of poetry? What is Sufism all about?
I come from an extremely local rural setting where such Sufi mystical practices openly defined my everyday life. It’s not about the technicalities and theories or institutionalised Sufi schools of their philosophies, this is more about what I learned from my childhood, and its physical surroundings dotted by several hybrid shrines. I’ve described this cultural setting in my 2013 Oxford University Press publication, The Festival of Pirs: Popular Islam and Shared Devotion in South India. This version of Sufism has more to do with everyday life rather than a spiritual domain.
You have lived away from your country for long, and yet the past seems to still haunt you. What is the identity you seek as a poet? Is it necessary to have a unique identity or can one be like a drop that flows and moulds as per the needs of the vessel?
In a way — physically– I’m away from my birth place, but in many ways, I’m also closer to my homeland than in my past. When I moved away from the actual picture, I see many dimensions from a new lens. Each dimension contributed to my rethinking and reconsidering the idea of India. As I wander around and meet totally different places and people, I learn more about my birthplace and moved a little closer to it. I totally understand this as a process to reconcile with the past and connect it to a new present intensified by many factors, not just personal. We’re living in a virtual world, which also looks like “real” in its sounds, colours and words. Every moment it makes me realise that I’m actually not that far. On the other hand, I also see the people in my homeland who are far more removed by their immediate reality and everyday experiences. We need to read this conditionality more in terms of perspective rather than physical distance.
You are fluent in Telugu, Urdu and English. You started writing in English and then moved to Telugu. And all your poetry collections have been in Telugu. Why? Would the outreach of English not have been wider? What made you pick Telugu over English?
Great question! My literary graph is neither linear nor simplistic. When I look back and reflect on it, it’s a quite messy roadmap — actually, there’s nothing like a map to get its contours. Yes, I started writing in English and then suddenly stopped sending out the poems to magazines. In fact, I write more in my personal journals rather than in print journals. Theoretically, I saw poetry as a personal diary for my experiences for many years. Due to financial concerns within my family, I had to start working very early on and left most of my journals at home. Then, my friends found them by chance and put them together that became my first collection of poems in Telugu. The collection was an instant success for its innovative style and then that opened up my career in Telugu rather than English which was my first language of literary expression.
You are now bringing out a bi-lingual online magazine, Saranga? What made you think of a magazine in two languages?
Before entering into teaching career, I worked as an editor of the literary supplement and Sunday magazine for a largest circulated Telugu newspaper. When we moved to the USA, I thought it would be better to have some outlet to engage with my home language and literature. In the early phase, Saranga was primarily a Telugu webmagazine. When I started teaching South Asian literature, then I realised the importance of making Indian literary texts available to contemporary generation in the USA. That was just one reason, but there’re were many factors as our team saw a rise in the Indian diaspora writings in the new millennium. Luckily, we got wonderful support from writers and poets in various Indian languages. The humble beginnings have actually ended up as a rewarding experience.
What is it you look for in contributors from two languages? Is it the same guidelines or different?
We’re still learning how this works! As it appears now, these two sections require two different approaches and guidelines. Since the English section has been now attracting writers from various languages, it’s moving more towards a multi-lingual base. We’re trying to accommodate more translations into English from different Indian languages. We still need to do lots of work there.
Is the journal only aimed at South Asian diaspora or would you be extending your services to all cultures and all geographies?
Saranga, as we see it right now, is more about South Asia and its diaspora. As you know, we need more such spaces for South Asia and its diaspora. Not sure about its future directions at this point, however, if the situation demands, we will extend its services further.
You have number of essays and academic books in English. But all your creative writing is in Telugu. Why? Would you be thinking of writing in English too because proficiency in the language is obviously not an issue?
Most of my academic writing came out of my teaching experience. As I started teaching new courses, I then realised that we need more material from South Asia. I started focusing on producing such materials primarily for my courses and then gradually, they became useful for many academicians elsewhere too. I still believe creating writing as a more personal space — that enables me to articulate more about myself. However, the publication of Evening with a Sufi, brought a new change — as I’ve been getting more requests for more writing in English for the last two years. As you know pretty well, I’m an extremely slow writer.
How do you perceive language as a tool for a poet?
I see language working many ways since I dwell in multiple languages. I started my elementary education in Urdu, and my middle school was in Telugu, and the subsequent studies were in English. Through the last day of her life, my mother was extremely particular about me learning Arabic and Farsi. So, I believe that helped me so much to understand how language works in a poem. When I published my first poem in Telugu, the immediate critique was it was a not a “Telugu” poem. Telugu literary critics labelled me as a poet who thinks either in Urdu or English, then writes in Telugu. Of course, most of them were also fascinated by the new syntax of my Telugu poems and the new images and metaphors—that totally deviate from a normative or mainstream Telugu poem of those days. The uses of language in a poem varies for each poet. If you’re reading, writing and thinking in just “one” language, that might be a safe condition. A contemporary or modern poet, however, belongs to many languages and cultures. We also migrate from one language to another in our everyday life.
Do borders of nationalism, mother tongue and geographies divide or connect in your opinion? Do these impact your writing?
The response to this question might be an extension to the above conditionality of a person. Anyway, I’m not a big fan of those ideas of nationalism, mother tongue and singular geographies. They don’t exist in my world. Most of my writings both creative and academic contest such boundaries and borders. To describe this in a single term- borderless. In fact, I believe we’re all borderless, but unfortunately, many boundaries and borders are now being imposed on our personalities.
(The online interview has been conducted by emails by Mitali Chakravarty)
Click here to access Afsar Mohammad’s poetry
source: http://www.borderlessjournal.in / Borderless / Home> Interview / by Mitali Chakravarty / July 14th, 2023